Three ways Minnesota’s failing electric bus fleets are debunking the arguments made by electric vehicle advocates
Evan Ramstad at the Star Tribune wrote a great story highlighting the multitude of entirely foreseeable potholes that electric buses are hitting in towns across Minnesota. The piece is solid journalism that debunks several of the lies electric vehicle (EV) advocates have told Minnesotans for years.
This article examines three of the common EV myths that are debunked by the lived experience of the Minnesota towns that have bought these buses.
Myth 1: EVs are cheaper to operate
Everyone knows electric buses cost about twice as much as diesel-powered buses. However, in 2021, Fresh Energy, a leading wind, solar, and EV misinformation group, wrote an article claiming that “EVs are cheaper to operate and maintain over their lifetime than their fossil fuel-powered counterparts.”
Transit officials in the Twin Cities and Duluth would beg to differ. The article by Ramstad indicated that e-buses are less efficient than diesel-powered buses they were meant to replace.
“We’re still paying more on a per-mile basis for electric than for diesel,” said Carrie Desmond, the head of electric bus infrastructure at Metro Transit in Minneapolis and St. Paul.
Myth 2: EVs are great winter vehicles
In November of 2023, Fresh Energy wrote an article called “Electric vehicles are great winter cars.” Apparently, the City of Duluth has had a vastly different experience.
In 2019, the Duluth Transit Agency (DTA) bought seven 40-foot buses, representing 10 percent of its fleet. Despite the fact that these e-buses cost $900,000, nearly twice as much as normal, diesel-powered buses, they were not able to do the same work as their conventional counterparts.
The Duluth system had to cut back the winter usage of e-buses because the cold temperatures and steep hills used so much electricity that the buses were not able to finish their driving shifts. The Minnesota Reformer noted that Duluth’s e-buses lost 60 percent of their range in the cold until they installed diesel-powered heaters on the buses to save battery charge.
The same occurred in the Twin Cities, as Metro Transit reported its electric buses lost 40 percent of their range in the winter. The Reformer noted “Any electric bus that operates in the state can’t truly be zero emissions for the foreseeable future, as both Duluth and Metro Transit’s electrics use diesel-fueled heaters to minimize the battery range loss.”
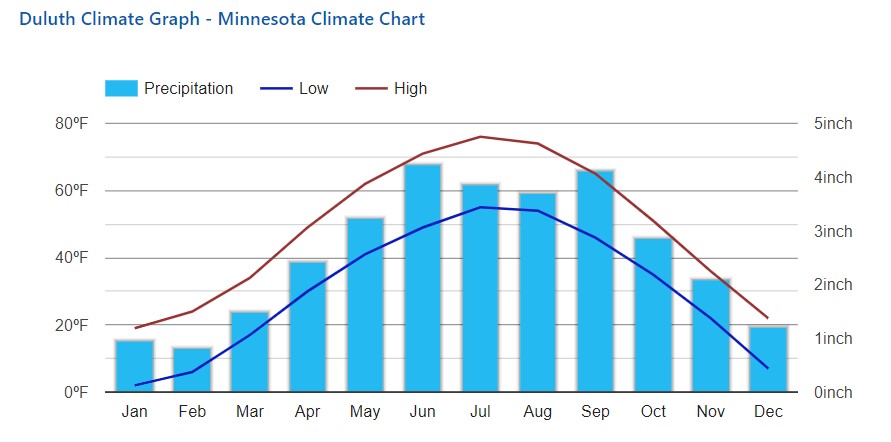
Duluth found that the e-buses performed best when the temperatures outside ranged from 40 to 65 degrees, which is unfortunate because the average high temperatures in Duluth are below 40 degrees for five months of the year, according to USClimateData.com.
Myth 3: EV batteries will quickly become exponentially better
Electric vehicle boosters and wind and solar advocates frequently argue that these technologies will experience exponential increases in efficiency, like the gains that occurred with microchips. The problem here is that nothing experiences that kind of efficiency growth except microchips. From the Strib article:
“There was a period of time when people in the industry were suggesting that the battery technology was going to evolve so fast that it would be kind of like semiconductors, maybe doubling at some predictable rate,” Brian Funk, chief operating officer for Metro Transit, said as we stood next to the 150-kilowatt chargers used for the 60-foot buses.
“That’s not been the experience,” Funk added. “We can get more battery and we can go farther than when we placed the order for these [buses], but it’s not orders of magnitude difference.”
All the challenges these electric bus initiatives are experiencing were entirely foreseeable because this expensive technology is not ready for primetime, a point that American Experiment has made for years.
The fact of the matter is electric vehicles are not a one-to-one replacement for conventional cars because they are not as convenient. This is a key reason why a new peer-reviewed paper found EVs are driven 4,477 fewer miles than conventional cars every year.
Using taxpayer-funded transportation dollars on EVs instead of traditional vehicles is a waste of money that results in poorer service for those who depend on public transit. Pretending otherwise is a denial of the facts on the ground.